DEFEAT PAIN
with
COUNTERSTRAIN
Has your pain or problem been resistant to other forms of treatment?
Neuro-fascial release maybe the answer!
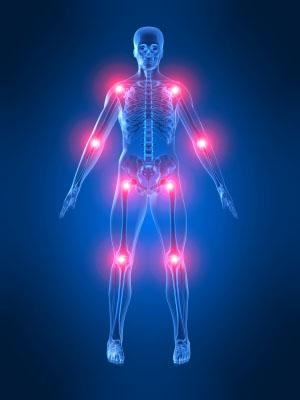
Fascia is a main source of pain
& dysfunction and connects
you from head to toe!
Learn more about this gentle but powerful way to rid the body of pain and dysfunction, while improving overall health.
Fascial Counterstrain
Drains the swampy (Interstitial Inflammatory Stasis - IIS) areas of your body of trapped inflammation and swelling that keeps your pain receptors firing and leads to acute & chronic dysfunction
2021 Article Excerpt - Why Counterstrain Works
Impaired Lymphatic Drainage and Interstitial Inflammatory Stasis in Chronic Musculoskeletal and Idiopathic Pain Syndromes: Exploring a Novel MechanismBrian Tuckey1*, John Srbely2, Grant Rigney3, Meena Vythilingam4 and Jay Shah5
- 1Department of Physical Therapy, Tuckey and Associates Physical Therapy, Frederick, MD, United States
- 2Department of Human Health and Nutritional Sciences, University of Guelph, ON, Canada
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Oxford University, Oxford, United Kingdom
- 4Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Health Innovation, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health, Washington, DC, United States
- 5Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Clinical Center, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States
"One promising intervention purported to deactivate nociceptors and alleviate tissue inflammation is Counterstrain (previously called Strain and Counterstrain) (135). Counterstrain utilizes cutaneous TPs/MTrPs to diagnose and treat MPS and idiopathic conditions. Once a TP is located, the body is gently placed into specific positions of ease that have been clinically identified to alleviate TP tension and tenderness. Tissue decompression (through positioning or local tissue manipulation) is believed to silence activated nociceptors, reducing the afferent barrage to the dorsal horn. Reduced nociception, deactivates segmental muscle guarding reflexes, reducing myofascial tension and capillary pressure. The treatment position is then maintained for up to 90 s to allow regional inflammation (interstitial pro-inflammatory cytokines) to gradually dissipate. Based on our hypothetical model, the associated reduction in interstitial NE concentrations during the release would also deactivate somato/visceral-sympathetic reflexes, helping to restore arterial and venous perfusion. Simultaneous reductions in IL-1b, IL-6 and TGF-b1 concentrations would normalize lymphatic propulsion and reduce myofibroblast (facial) contraction blocking pre-lymphatic pathways.
The impact of Counterstrain on inflammation has been investigated at the cellular level, demonstrating improvements in tissue morphology. Researchers repetitively strained human fibroblasts for 8 h in a two-dimensional tissue matrix while measuring the effects on fibroblasts, including cytokine production. A 60-second Counterstrain (or indirect osteopathic manipulative treatment) was then applied which produced beneficial effects on fibroblast morphology, reversing the inflammatory effects (46% reduction in fibroblast IL-6 production after 24 h) when compared to control (136). Recently Counterstrain has been renamed Fascial Counterstrain and expanded to include over 800 anatomically named structures, treatments, and diagnostic TPs. This pain-free, non-invasive treatment warrants further investigation as it may have the capacity to alleviate microvascular stasis in all tissues, breaking the feed-forward cycle that creates myofascial pain and potentially idiopathic visceral/vascular syndromes.+
Front. Pain Res., 23 August 2021
Sec.Musculoskeletal Pain
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpain.2021.691740
Easy to Understand Fascial Counterstrain Video
|
|
|
|
Shoulder Injury
|
Concussion
|
Easy on-line scheduling 24 hours a day.